
How Solar Panels Work: Harnessing The Power Of The Sun
Globally, solar panels provide clean and renewable energy to power our homes, businesses, and communities. Do you ever wonder how these sleek, shiny panels convert sunlight into electricity? Our blog will explore the fascinating world of solar panels and the science behind their operation.
The Basics of Solar Panels
Solar panels, also known as photovoltaic (PV) panels, are devices that convert sunlight into electricity through a process known as the photovoltaic effect. This phenomenon was first discovered in the 19th century, but it wasn’t until the mid-20th century that practical solar cells were developed.
- Photovoltaic Cells: At the heart of a solar panel are many individual photovoltaic cells, also called solar cells. These cells are typically made from semiconductor materials, most commonly crystalline silicon. Silicon is chosen for its efficiency in converting sunlight into electricity.
- Absorption of Sunlight: Solar panels are designed to absorb sunlight, specifically the energy carried by photons, which are particles of light. When sunlight strikes the solar cells, the photons are absorbed by the semiconductor material.
- Generation of Electrons: When photons are absorbed, they transfer their energy to electrons in the semiconductor material, allowing these electrons to break free from their normal positions in the atoms.
- Electric Current: The flow of these energized, free electrons creates an electric current, which can be harnessed and used as electricity. This flow of electrons is directed through an electrical circuit within the solar panel.
Key Components of a Solar Panel
To better understand how solar panels work, let’s explore their essential components:
- Solar Cells: As mentioned earlier, solar cells are the fundamental building blocks of a solar panel. They consist of a thin layer of semiconductor material, usually silicon, with electrical connections on the top and bottom.
- Anti-Reflective Coating: Solar panels have an anti-reflective coating on their surface, which helps maximize the amount of sunlight that is absorbed rather than reflected away.
- Front and Rear Contacts: These are metal conductive layers on the top and bottom of each solar cell. They allow the free electrons generated by the photovoltaic effect to flow out of the cell and create an electric current.
- Encapsulation: Solar panels are encapsulated in a protective layer, usually made of glass, to shield the cells from environmental factors such as dust, moisture, and physical damage.
- Frame and Backsheet: The frame provides structural support for the panel and ensures its durability. The back sheet is another protective layer on the back of the panel.
The Role of Inverters
While solar panels generate direct current (DC) electricity, most of our appliances and the grid use alternating current (AC). To make the electricity generated by solar panels compatible with our homes and the grid, an inverter is used. Inverters convert DC electricity into AC electricity, ensuring that the energy produced by solar panels can power our lights, appliances, and other electrical devices.
How Solar Panels Work on a House
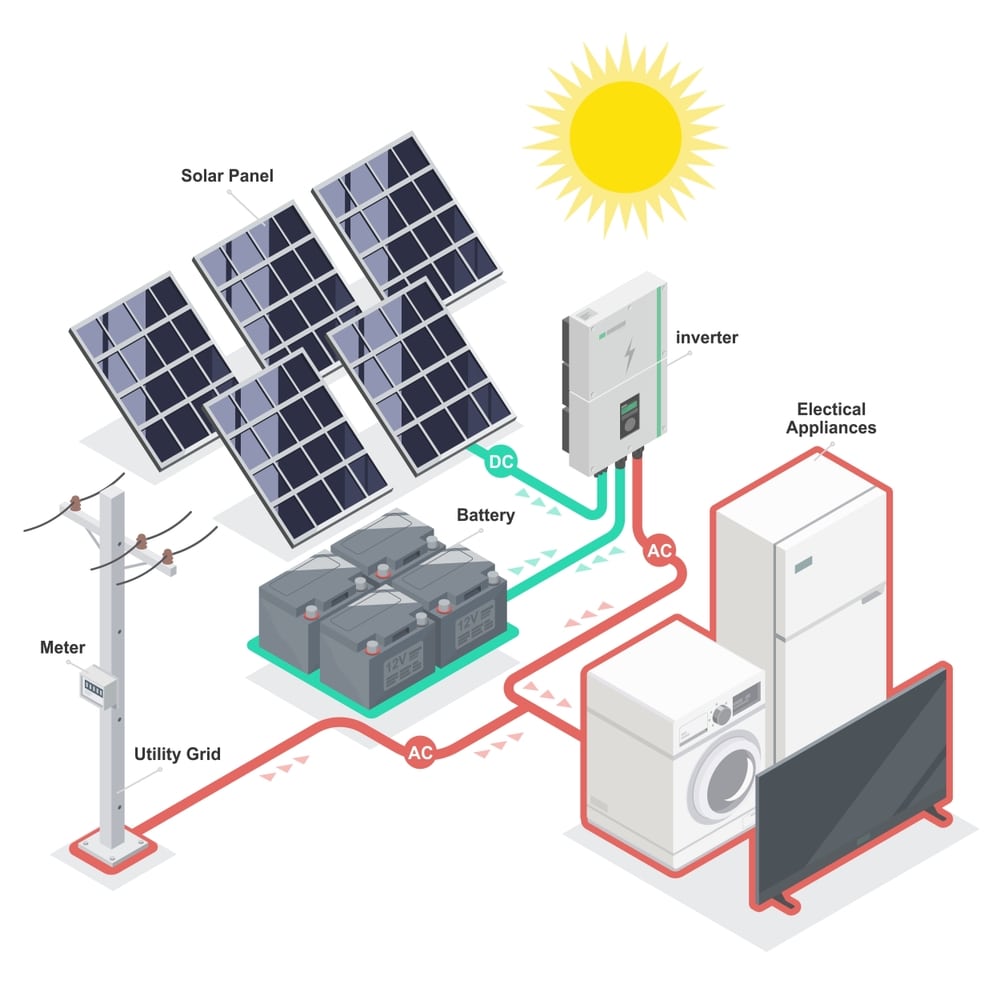
Solar panels on a house are a sustainable and environmentally friendly way to generate electricity, reduce energy bills, and contribute to a greener future. Here’s a brief overview of how solar panels work on a residential property:
- Sunlight Absorption: Solar panels, typically installed on the roof of a house, are designed to capture sunlight. These panels consist of numerous solar cells made of semiconductor materials like silicon.
- Photovoltaic Effect: When sunlight strikes the solar cells, it energizes electrons within the cells, causing them to become free from their usual positions in atoms. This process, known as the photovoltaic effect, generates an electric current.
- Direct Current (DC) Generation: The electric current produced by the solar cells is initially in the form of direct current (DC). This type of electricity flows in one direction, and it’s the same kind of electricity produced by batteries.
- Inverter Conversion: Most household appliances and the electrical grid use alternating current (AC). To make the electricity generated by solar panels compatible with these systems, an inverter is used. The inverter converts the DC electricity into AC electricity.
- Power Usage: The converted AC electricity can now be used to power the lights, appliances, and electrical devices in the house. Any excess electricity not immediately used is often fed back into the electrical grid, depending on the specific setup and local regulations.
- Net Metering (Optional): In some regions, a net metering system is employed. This allows homeowners to receive credit for excess electricity sent back to the grid, effectively reducing their electricity bills or even earning them money.
- Energy Storage (Optional): Some homeowners choose to incorporate energy storage solutions, like batteries, into their solar panel systems. These batteries store excess electricity generated during sunny days for use during the night or when the sun isn’t shining.
- Monitoring and Maintenance: Modern solar panel systems often come with monitoring tools that allow homeowners to track the system’s performance and energy production. Routine maintenance, such as cleaning the panels and ensuring they are free from shading, is essential to maximize efficiency.
Conclusion
Solar panels work by harnessing the power of sunlight through the photovoltaic effect, generating electricity that can be used to power homes, businesses, and more. As technology continues to advance, solar panels are becoming increasingly efficient and affordable, making solar energy a crucial player in the transition to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly energy future. Pakistan’s abundant sunlight, solar energy systems have the potential to deliver substantial cost savings and reduce dependence on fossil fuels, Solar system installation services in Karachi have witnessed significant growth in recent years, reflecting the nation’s commitment to harnessing renewable energy sources and addressing energy shortages. we appreciate the elegance of this renewable energy source and its potential to reduce our reliance on fossil fuels while reducing our carbon footprint.
Solar panels on a house work by converting sunlight into electricity through the photovoltaic effect. This electricity is then transformed into the alternating current (AC) required for household use, either directly powering the home’s electrical needs or feeding surplus energy into the grid. Solar panels not only reduce electricity bills but also contribute to a cleaner and more sustainable energy future for homeowners and the planet.